Your Location:Home > Products > Organic chemicals
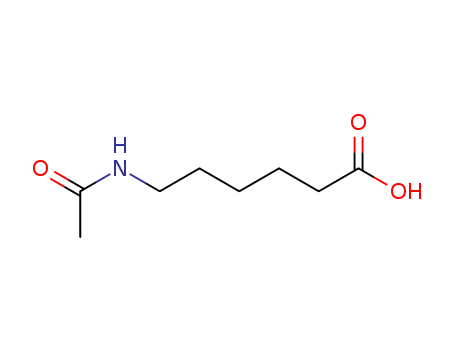

CasNo: 57-08-9
MF: C8H15 N O3
Appearance: White.
|
Manufacturing Process |
400 L of demineralized water, 5.0 kg of calcium hydroxide, and 155.0 kg (1000 moles) of acetyl-caprolactame are introduced under stirring and at a temperature of about 25°C into a 1000 L stainless double walled reactor. The temperature is raised to 30°C. 75.0 kg of calcium hydroxide are introduced stepwise in the form of successive amounts of 2.0 kg each in the medium, under stirring and at a temperature adjusted and maintained 25°- 30°C through external cooling, in a manner such that the time required to introduce into the reactor the whole amount of calcium hydroxide approximates 1.5 h. When the stirring is stopped, the pH is about 7.5-7.8. The obtained mixture is stirred continuously at a temperature of 30°C during 14 h. At the end of this operation the pH is again adjusted at a value 7.5-7.8. The hydrolysate is filtered on a 60 x 60 pressfilter comprising 6 compartments and equipped with fabrics of the polyester known under the designation TERGAL which have been previously coated with a suspension of a cellulose commercialized under the trademark SOLKA FLOX BW20. The duration of filtration is of 1.5 h. 580 L of the filtrate are recovered and subjected to a concentration under reduced pressure in an evaporator the volume of which is of 750 L, at a distillation temperature ranging from 45°-50°C under a reduced pressure of 10-15 Torr. The operation is ran until concentration of the solution to 280 L, the concentrated solution being then left standing. The crystallisation is already considerable 2 h after the end of the operation of concentration. Crystallisation is ended after 16-24 h. The crystals are centrifuged at a speed of 700 revolutions/minute. The centrifuged crystals of calcium acexamate are washed twice on the centrifuge with 20 l of acetone. 107.0 kg of crystals are obtained, which are dried under vacuum at 40°C. The 96.0 kg of dry calcium acexamate obtained are ground and sifted. Acexamic acid may be produced by treatment of the calcium acexamate with HCl. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Antifibrinolytic |
InChI:InChI=1/C8H15NO3/c1-7(10)9-6-4-2-3-5-8(11)12/h2-6H2,1H3,(H,9,10)(H,11,12)/p-1
Human serum albumin has been specificall...
Friedel-Crafts acylation of ferrocene wi...
The present disclosure relates to imagin...
Amine dehydrogenases (AmDHs) catalyse th...
The invention discloses a method for syn...
The acidity of N-acyl amino acids is dep...
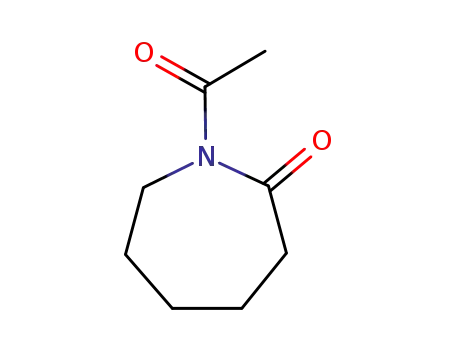
N-acetylcaprolactam

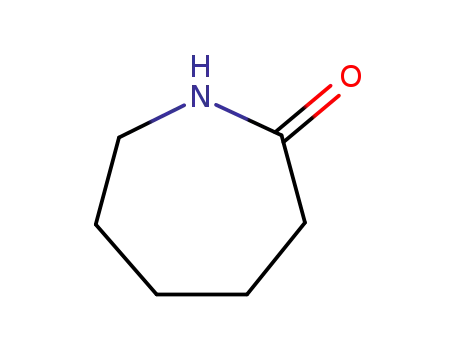
caprolactam
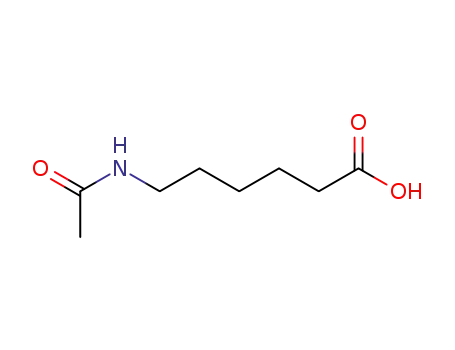
6-(acetylamino)hexanoic acid

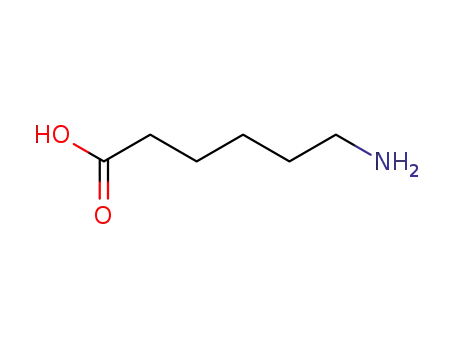
6-aminohexanoic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
water;
at 100 ℃;
Product distribution;
different time of hydrolysis;
|
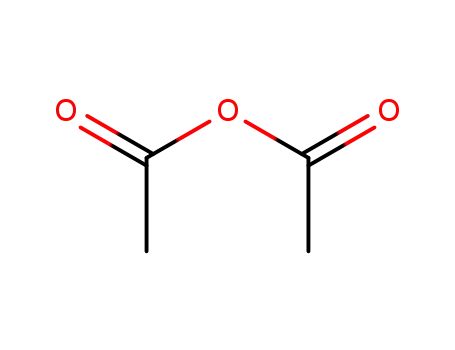
acetic anhydride


6-aminohexanoic acid


6-(acetylamino)hexanoic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
at 0 - 20 ℃;
|
79% |
|
With
pyridine;
In
benzene;
|
|
|
In
dichloromethane;
for 0.5h;
|
|
|
With
dmap;
at 20 ℃;
for 0.5h;
|

N-acetylcaprolactam

acetic anhydride

6-aminohexanoic acid
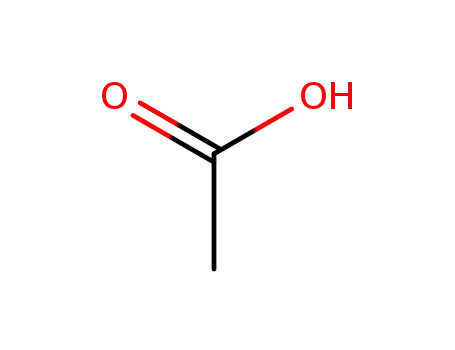
acetic acid
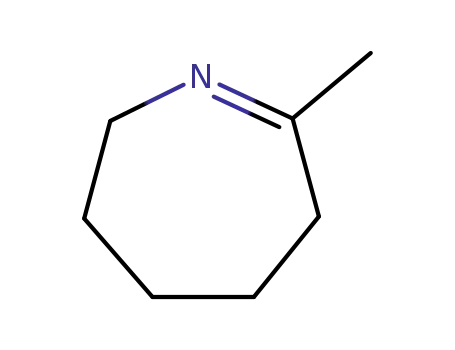
2-methyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-3H-azepine

caprolactam

6-aminohexanoic acid
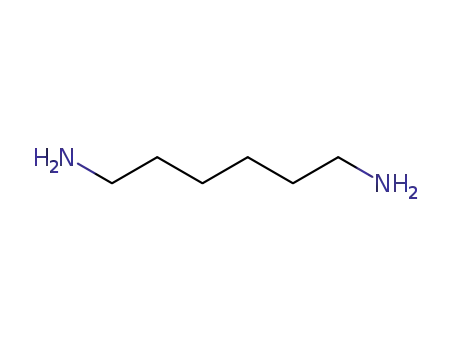
1,6-Hexanediamine